Stoichiometry
Due to the inherent complexity and dynamic nature of macromolecular assemblies, determining the stoichiometry of protein complexes poses a significant challenge. MDS can unravel the complex puzzle of protein stoichiometry, providing crucial insights into their structural organization to understand biological processes and the mechanism of action of drug candidates.
Overview
Cellular processes dependent on the presence of precise amounts of specific proteins and their complexes. The stoichiometry for a protein complex is the description of the individual protein subunits. Determining stoichiometry of a given complex, such as the number of antibodies bound to an antigen, helps to understand the overall function of that complex. In drug development, the stoichiometry of a drug–target interaction is often closely linked to the drug’s mechanism of action and is thus crucial for the development of highly effective and safe therapeutics.
MDS provides stoichiometry of challenging interactions
Case Study
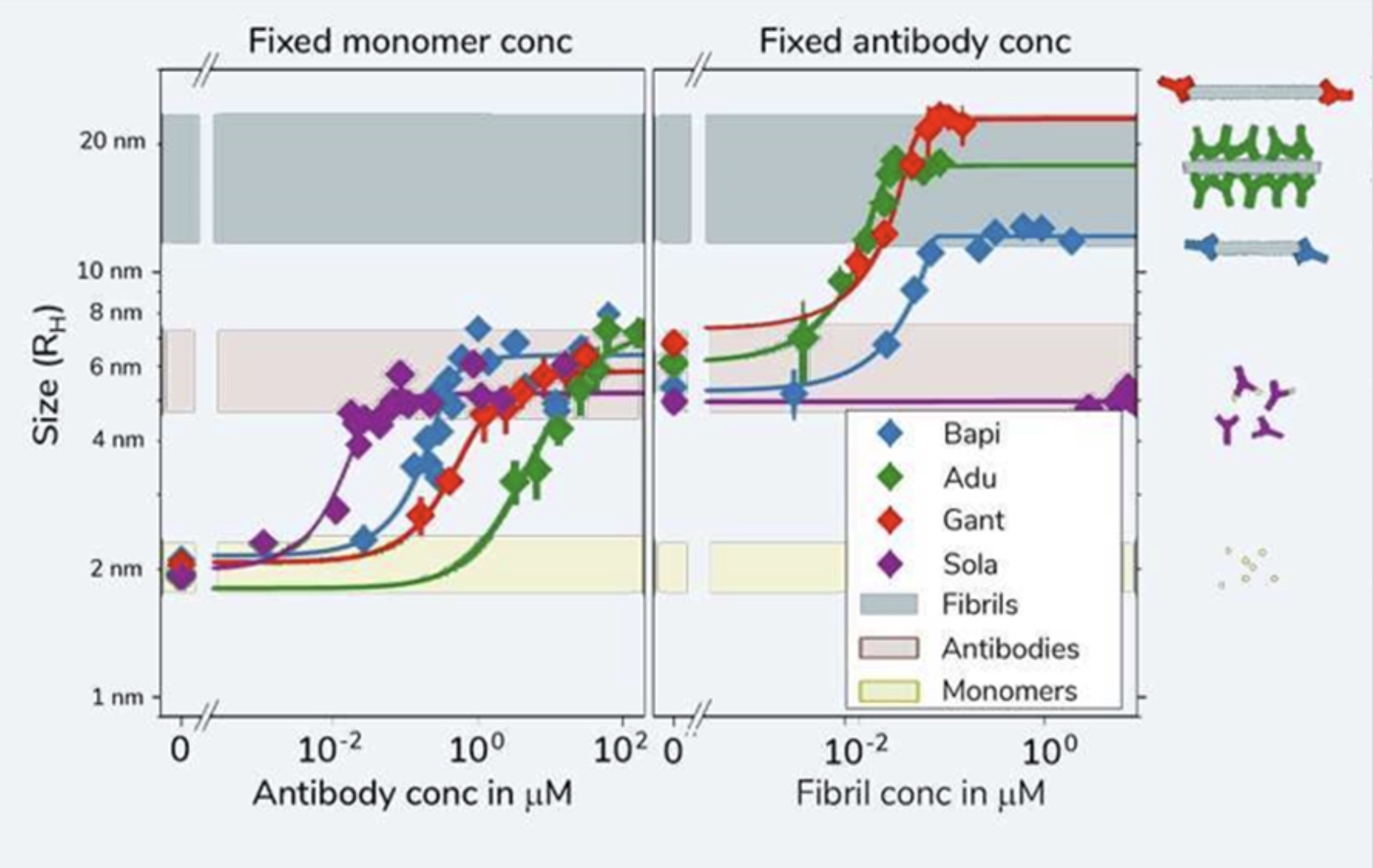
Kinetic fingerprints differentiate the mechanisms of action of anti-Aβ antibodies.
Linse et al., Nature Struct. Mol. Biol., 2020, 27, 1125–1133. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-020-0505-6
During our research into protein amyloid formation, we have used many different techniques for assessing protein interactions – all with different limitations and advantages. With diffusional sizing, we were able to confidently generate accurate and complete in-solution data using amyloid proteins to connect stoichiometry and binding affinities with protein self-assembly. The data could provide key insights for novel therapeutic approaches in Alzheimer’s disease.
Get started
To study intrinsically-disordered, aggregated proteins, or any biological interaction in their native state in solution we recommend the following:
Workflow specification and benefits:
- 25 min run time
- KD range from pM to µM
- Provides stoichiometry
- Amount of antibody or binding partner 1-10µg depending on affinity
- Amount of target 10-25µg
- 12 µl of sample per triplicate
- Use of complex background e.g., serum, lysate, CSF
- Quick & easy to perform.