Intrinsically disordered proteins
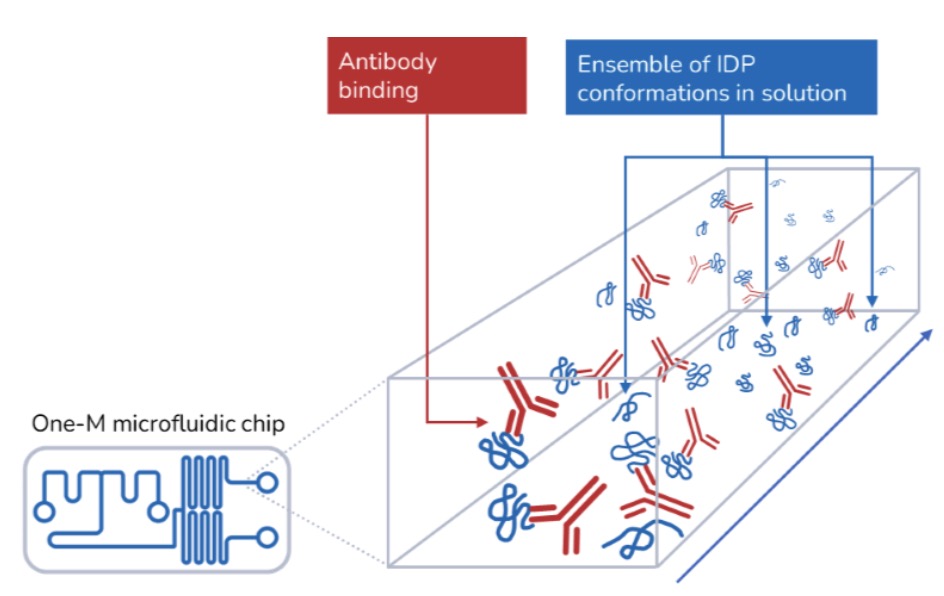
Characterizing intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) is challenging due to their lack of stable structures, making traditional structural and functional characterization methods less applicable. MDS offers studying such challenging targets directly in solution and bypasses restrictions associated with surface-based methods.
Overview
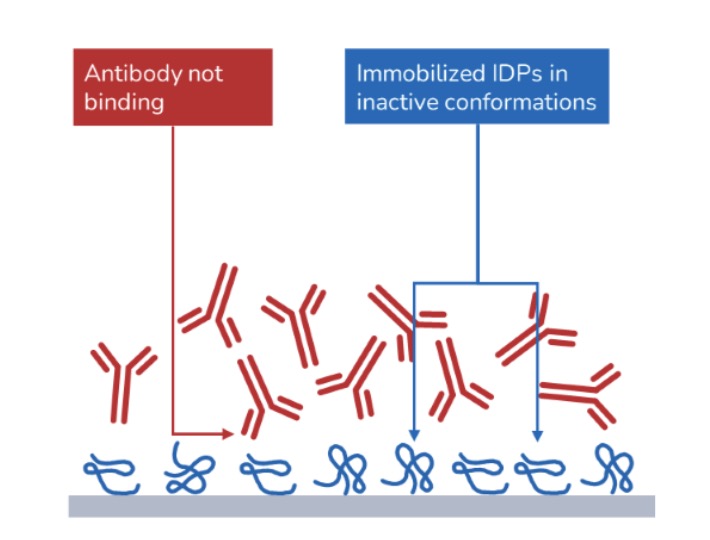
Intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) lack a well-defined three-dimensional structure under physiological conditions. Instead, they exist as dynamic ensembles of conformations and play crucial roles in various cellular processes, often involving interactions with other proteins, nucleic acids, or small molecules. Due to their inherent flexibility and ability to adopt multiple conformations, IDPs are implicated in a wide range of disease areas such as neurodegenerative disease, oncology, or viral infections. To understand IDP interactions, tethering them to a surface can be problematic and does not replicate the dynamic and flexible nature of IDPs in their native environment, limiting the relevance and accuracy of the obtained data. Microfluidic diffusional sizing (MDS) avoids surface immobilization and thus preserves the native flexibility and dynamic behavior of IDPs reducing the risk of inducing artificial structures and provides a more accurate representation of the IDPs’ behavior and interactions.
MDS benefits over surface immobilization methods
Case Study
Kinetic fingerprints differentiate the mechanisms of action of anti-Aβ antibodies.
Linse et al., Nature Struct. Mol. Biol., 2020, 27, 1125–1133. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-020-0505-6
During our research into protein amyloid formation, we have used many different techniques for assessing protein interactions – all with different limitations and advantages. With diffusional sizing, we were able to confidently generate accurate and complete in-solution data using amyloid proteins to connect stoichiometry and binding affinities with protein self-assembly. The data could provide key insights for novel therapeutic approaches in Alzheimer’s disease.
Get started
To study intrinsically-disordered or aggregated proteins in their native state in solution we recommend the following:
Workflow specification and benefits:
- 25 min run time
- KD range from pM to µM
- Provides stoichiometry
- Amount of antibody 1-10 µ g depending on affinity
- Amount of oligomer or fibril 10-25 µ g
- 4 µ L of sample
- Use of complex background e.g. serum, lysate, CSF
- Quick & easy to perform